Induction Brazing an Aluminum Assembly
Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
Applications
Applications: More
Applications: More

Industries:
Industries: More
Industries: More
Industries: More

Products:
Products: More
Services:
Services: More

Learn:
Learn: More
About:


A client in the energy storage technology market turned to Ambrell because they needed to heat non-magnetic steel tubing. Given their requirements, THE LAB at Ambrell determined that an Ambrell EASYHEATTM 4.2 kW, 150-400 kHz induction heating power supply with a custom-designed single position multiple-turn helical coil was the right solution for their application.
Initial tests were conducted to optimize the power delivered to the part. An infrared camera was used to observe the mesh temperature inside the tube. It was observed that the tube reached temperature within a minute. The mesh inside reached approximately 1022 °F (550 °C) within 5 minutes and remained at that temperature to 10 minutes, at which point the experiment concluded. A good heating pattern was achieved and the results met the client's objectives.
THE LAB successfully confirmed the viability of this application. Induction's speed of heating was a key factor as was the solid, repeatable results that it delivered. Finally, THE LAB's expertise was also critical. To learn more about complimentary induction heating testing from THE LAB at Ambrell, visit our website. Or click the image below to check out application notes from THE LAB. 

Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
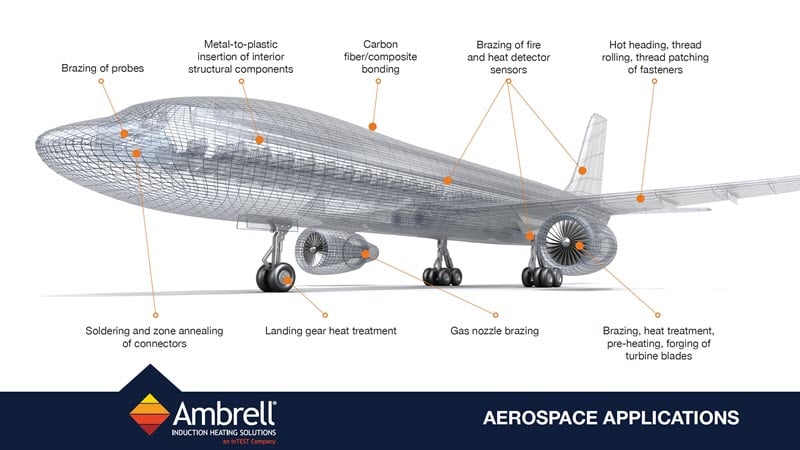
Induction heating is a process that uses electromagnetic fields to heat electrically conductive materials. It has been used in numerous industries...

Induction heating, a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat electrically conductive materials, is often thought of for large industrial...