Induction Brazing an Aluminum Assembly
Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
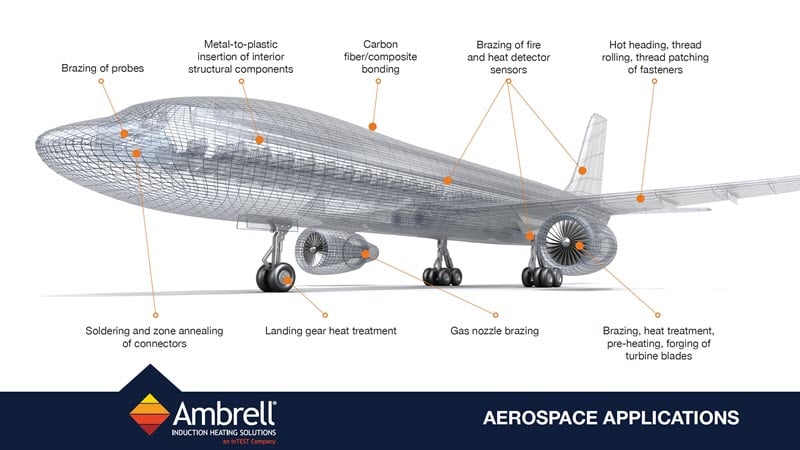
Applications
Applications: More
Applications: More

Industries:
Industries: More
Industries: More
Industries: More

Products:
Products: More
Services:
Services: More

Learn:
Learn: More
About:


Induction heating has many uses and applications, one of which involves the process of induction hardening. The top three benefits of induction hardening are:
fast heating cycles
accurate heating patterns
cores that remain relatively cold and stable
But before you invest in an induction solution for induction hardening, it's important to understand how the process works. Here's part one of our beginner's FAQ about induction hardening.
Induction hardening is a heat treatment method that involves the heating of a metal part using induction and quenching. The quenched metal goes through a process called a martensitic transformation, which increases both the hardness and brittleness of the metal part.
When used in the context of induction hardening and heat treating processes, quenching refers to the rapid cooling of a metal piece or workpiece in either water, air, or oil in order to bring about specific qualities. Quenching prevents phase transformations and other undesired low-temperature processes from occurring by minimizing the time span in which these processes are kinetically available and thermodynamically ideal.
The process of induction hardening is most commonly used in steel alloys. This ie because there are many mechanical parts, including gears, shafts, and springs, that are subjected to surface treatments prior to delivery in order to enhance what is known as wear behavior. However, it's important to keep in mind that the level of effectiveness of any given induction hardening treatment depends on a variety of factors, including the modification of surface material properties and the introduction of residual stress. But above all, the process is known to be one of the most effective and widely employed processes meant to increase component durability.
The principles of induction heating have been applied to manufacturing since the 1920s. Understanding the facts about induction heating equipment and applications such as induction hardening is the key to determining which heat treatment methods are right for your needs. Keep an eye out for the next post, where we'll answer some more common questions about induction heating equipment and hardening processes.

Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
Induction heating is a process that uses electromagnetic fields to heat electrically conductive materials. It has been used in numerous industries...
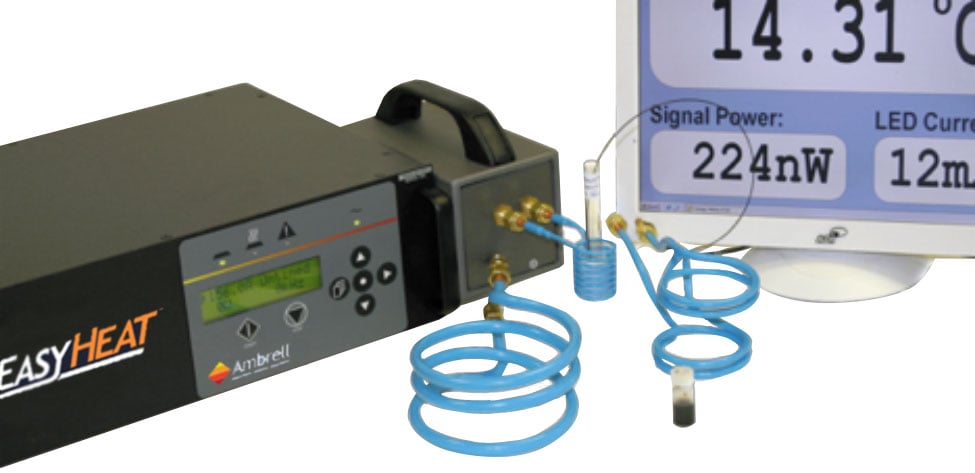

Induction heating, a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat electrically conductive materials, is often thought of for large industrial...