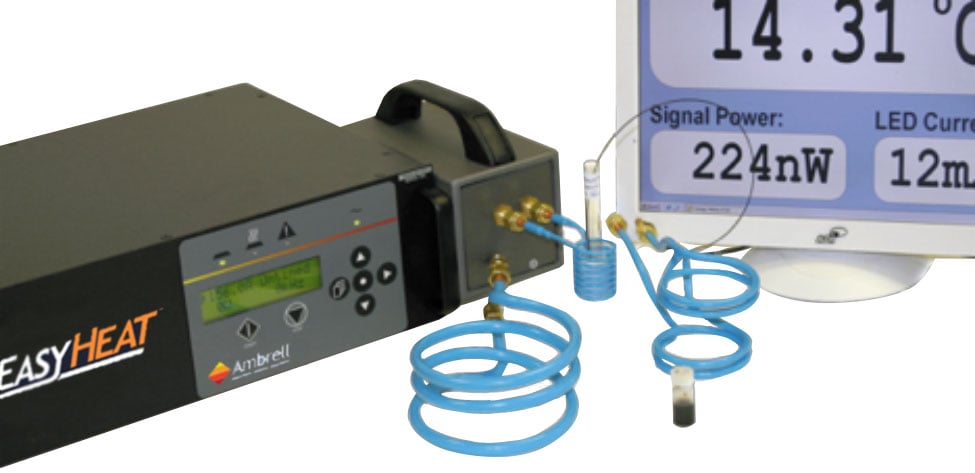
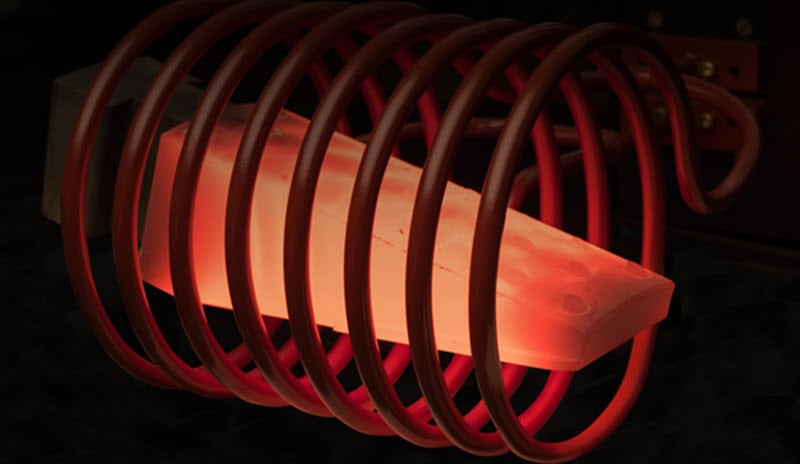
The basic principles of induction heating have been used in manufacturing since the 1920s. Induction brazing is just one process that uses the science of induction heating to fuse metals. Before you get started with induction brazing, it's important to understand how the process works. Let's look at some answers to common questions about induction brazing.
What is induction brazing?
Induction brazing is a process that involves the fusing of two or more materials using a filler metal with a lower melting point than the base materials. During the induction heating process, the materials, which are usually ferrous, are heated quickly from the surrounding electromagnetic field that the alternating current creates from the induction coil.
Which materials are suitable for induction brazing?
There are a number of materials that can be used in the processes and applications of induction brazing. Metallic materials are among the most common due to their even heating properties. Keep in mind that when materials made of ceramic are involved, heating is more likely to occur as a result of conduction from the surrounding metallic components.
Silver is also frequently used as a filler metal during the induction brazing process. This is because it has a low melting point. For instance, silver-copper eutectic brazes have melting temperatures between 1100 and 1650 degrees Fahrenheit (593-899 °C). Aluminum brazing filler metals are less common and have a melting temperature of 1050 degrees to 1140 degrees Fahrenheit (566-616 °C). Copper braze alloys are the least expensive and have a melting point between 1300 and 2150 degrees Fahrenheit (704-1177 °C).
What are some of the main benefits of induction brazing?
The efficiency of an induction heating system for a specific application depends on four factors: the characteristics of the part itself, the design of the inductor, the capacity of the power supply, and the amount of temperature change required for the application. That being said, there are a number of benefits that come with using induction brazing in industrial applications. The primary benefits include improved joint quality, selective heating abilities, and quicker heating cycles. Induction brazing is also known for producing more consistent results and being more suitable for the production of larger volumes.
Ultimately, knowing how induction brazing works can help you make the best decisions for your industrial heating application needs. For more information about induction brazing, including how to braze aluminum, contact Ambrell Corporation.