Why choose induction over an oven for manufacturing?
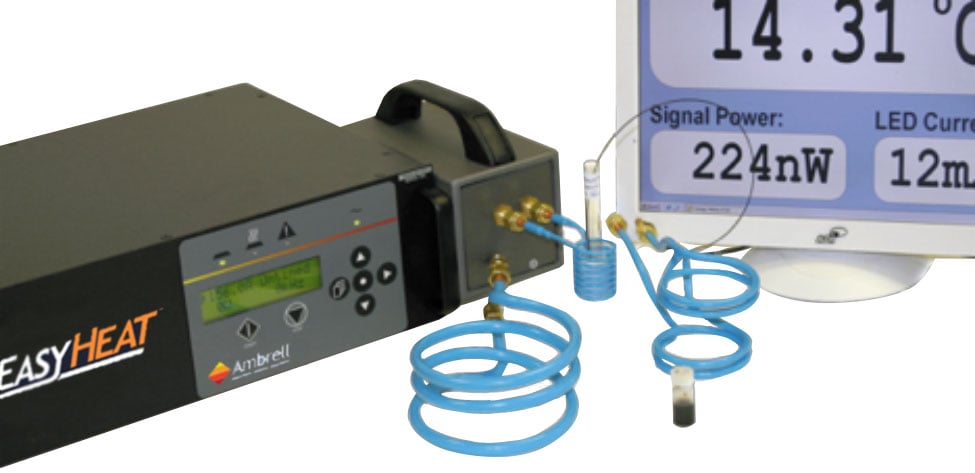
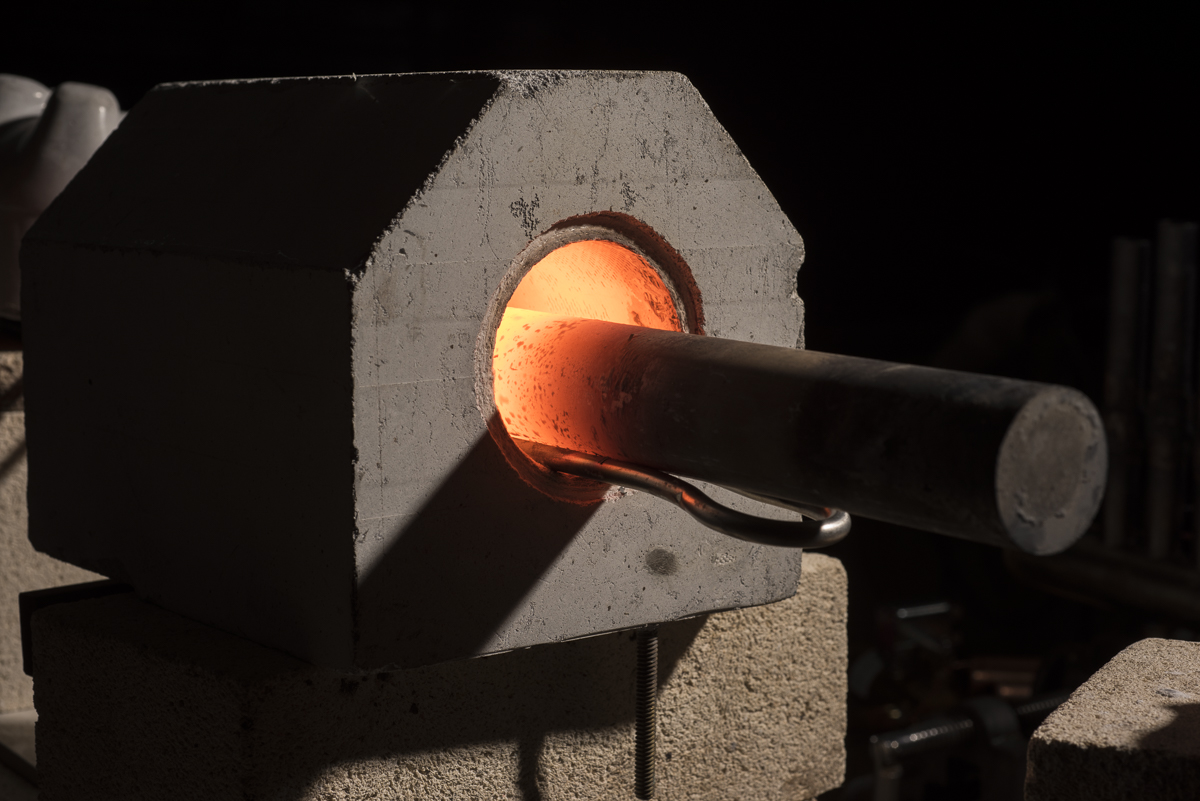
Induction heating is a precise, fast, repeatable, non-contact method for heating electrically-conductive materials like brass, aluminum, copper or steel or semiconducting materials such as silicon carbide. It is also an efficient, clean and environmentally-friendly process, as it does not produce any emissions. Those are just some of the reasons induction heating has become increasingly popular in manufacturing.
Now, let's look at some of the specific reasons why manufacturers choose induction heating over oven heating:
- Efficiency: Induction heating is an efficient way to heat metals. Up to 90% of the energy used in induction heating is converted into heat, compared to only about 50% for oven heating. This means that induction heating can save manufacturers a significant amount of money on energy expenses.
- Precision: Induction can be very precisely controlled, which is important for many manufacturing applications. For example, induction heating can be used to heat specific areas of a part without affecting the surrounding areas. This can be difficult to achieve with an oven.
- Cleanliness: Induction is a very clean process. It does not produce any emissions, such as smoke or fumes. This makes it an ideal choice for manufacturing applications where cleanliness is important, such as food and drug manufacturing.
- Environmental friendliness: Induction heating is an environmentally friendly process. It does not produce any greenhouse gases or other pollutants. This makes it a good choice for manufacturers who are looking to reduce their environmental impact and meet carbon neutrality goals.
Additional benefits of induction heating
In addition to the benefits listed above, induction heating also offers a number of other advantages, including:
- Faster heating times: Induction heating can often heat metals faster than oven heating. This can lead to significant time savings and more throughput for manufacturers.
- Reduced distortion: Induction heating causes less distortion in metals than oven heating. This is important for applications where dimensional accuracy is required.
- Improved repeatability: Induction heating is a very repeatable process. This means that manufacturers can produce consistent results time after time.
- Footprint: Induction tends to require significantly less space than an oven. And it can be even more advantageous when you consider that the induction workhead can be placed a distance from the induction power supply.
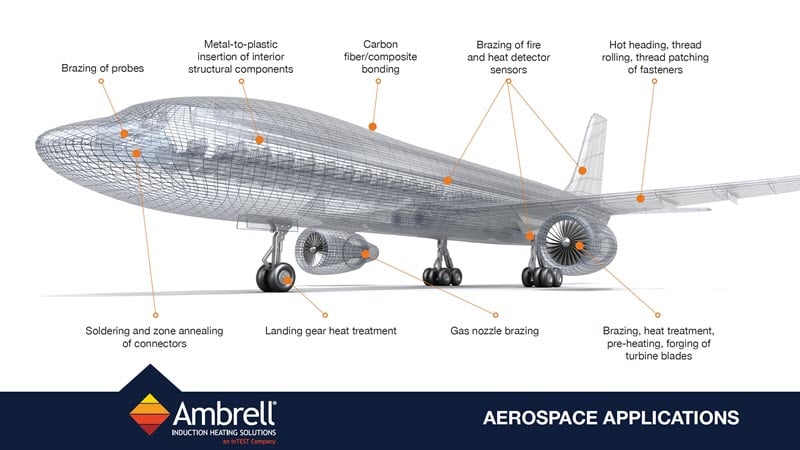
Common applications of induction heating
Induction is used in a wide variety of manufacturing applications, including:
- Brazing and Soldering: Induction heating can be used to join metals, such as soldering and brazing. These are often great applications for induction.
- Forging: Induction heating can be used to heat metals prior to forging.
- Heat treatment: Induction heating can be used to heat treat metals, including hardening, annealing, and tempering.
- Melting: Induction heating can be used to melt metals.
- Surface treatment: Induction heating can be used to apply surface treatments to metals, such as coatings.
Induction heating is an efficient, precise, clean, and environmentally friendly way to heat metals. It offers a number of advantages over oven heating, including faster heating times, reduced distortion, improved repeatability, and safety. Induction heating is used in a wide variety of manufacturing applications, including heat treatment, heat staking, forging, joining, melting, and surface treatment.
Learn more about induction on our About Induction page.




Brett Daly
9/29/23 2:26 PM