Induction Brazing an Aluminum Assembly
Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
Processes
Processes: More
Processes: More

Industries:
Industries: More
Industries: More
Industries: More

Products:
Products: More
Services:
Services: More

Learn:
Learn: More
About:


There is always demand for stronger, safer, and more efficient materials. Induction heating can play an important role in the process of finding better solutions. In this article we'll take a look at the role induction heating can play and showcase its benefits when being used for this important task.
Traditional heating methods like torches or furnaces often lack precision and can deliver unwanted variables. But induction heating bypasses many of the pitfalls of those heating methods and offers:
Focuses heat on specific areas, minimizing unwanted thermal effects on the surrounding material.
Reaches desired temperatures in seconds, accelerating testing procedures.
Eliminates open flames and fumes, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
Works across various materials, from metals to composites, expanding testing possibilities.
Less energy consumption and reduced emissions contribute to a greener testing process.
Now, let's look at how induction heating plays an important role in different aspects of material testing:
Simulate real-world stresses by precisely heating specific areas before tensile, fatigue, or creep testing.
Measure thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, and melting points with accuracy and control.
Study grain size, phase transformations, and other important microstructural changes induced by heating.
Identify the root cause of material failures by replicating specific thermal conditions that led to breakdown.
Evaluate the performance of coatings, treatments, and surface modifications under controlled heating conditions.
Numerous industries are using induction heating to develop stronger and better materials. Here we'll look at just a few of them:
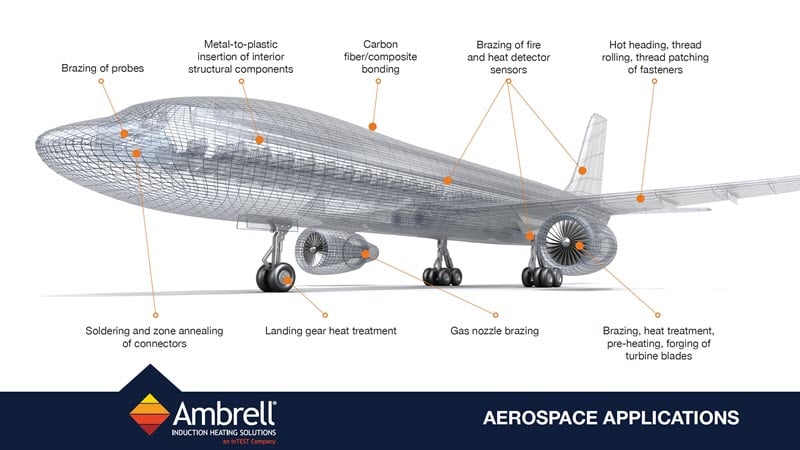
Design lighter, stronger aircraft components that can withstand extreme temperatures and conditions.
Build more fuel-efficient cars with parts that are durable and heat resistant.
Create reliable circuitry and heat sinks for high-performance devices.
Develop safer and more durable implants and medical devices.
Enhance the performance and longevity of building materials in diverse environments.
As the demand for better materials intensifies, induction heating's role in testing will become even more critical. Its precision, speed, and versatility make it an invaluable tool for developing the next generation of materials that are stronger, safer, and more sustainable.
Have you explored the power of induction heating in your material testing endeavors? Contact us today to learn more and discuss what solution might work for your material testing applications.

Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
Induction heating is a process that uses electromagnetic fields to heat electrically conductive materials. It has been used in numerous industries...
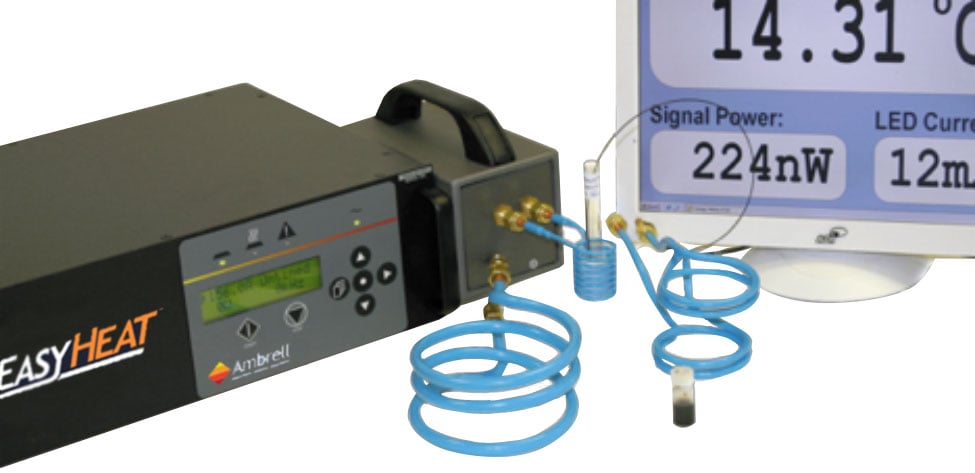

Induction heating, a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat electrically conductive materials, is often thought of for large industrial...