Induction Brazing an Aluminum Assembly
Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
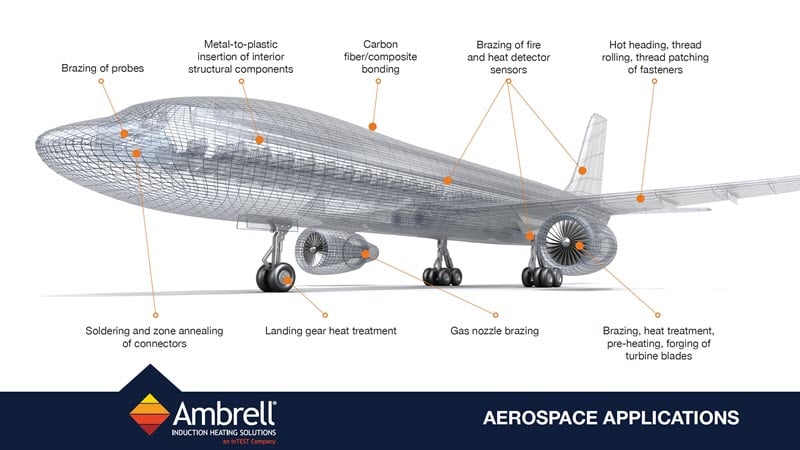
Applications
Applications: More
Applications: More

Industries:
Industries: More
Industries: More
Industries: More

Products:
Products: More
Services:
Services: More

Learn:
Learn: More
About:

1 min read
Brett Daly
12/5/17 4:00 PM


Induction heating is a process used in countless applications and industries. But before you get started with your own applications for induction heating, it's useful to have a clear understanding of how the process works. Here's a quick FAQ to help you understand the basics of induction heating.

Objective A company wanted to assess using induction heating for their aluminum assembly brazing process, and contacted THE LAB at Ambrell to utilize...
Induction heating is a process that uses electromagnetic fields to heat electrically conductive materials. It has been used in numerous industries...
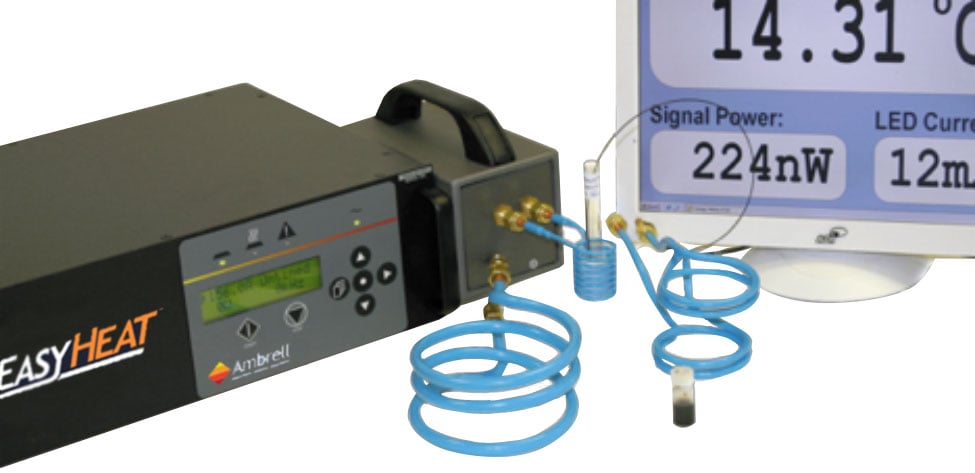

Induction heating, a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat electrically conductive materials, is often thought of for large industrial...