How Researchers and Universities Use Induction Heating
Induction heating, a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat electrically conductive materials, is often thought of for large industrial...
Applications
Applications: More
Applications: More

Industries:
Industries: More
Industries: More
Industries: More

Products:
Products: More
Services: More

Learn:
Learn: More
About:

1 min read
Justyna Bakker
10/27/15 7:40 AM
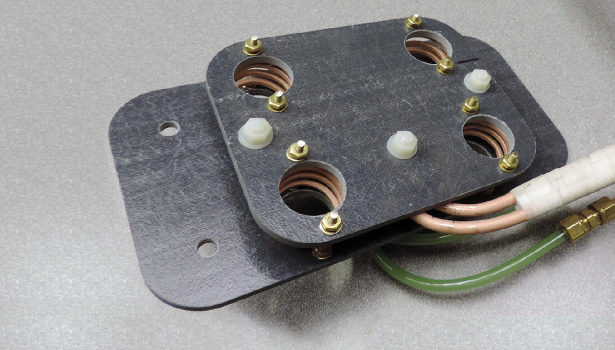
Metal to plastic insertion (also called heat staking or indirect induction heating) is a popular induction heating application at Ambrell's worldwide application laboratories. Dr. Girish Dahake, Senior Vice President of Global Applications, and his team have seen this application with great frequency. He published an article in Industrial Heating on the topic, and here are eight critical parameters that he highlighted for a consistent induction insertion process:
The frequency of operation of the power supply should be chosen to deliver efficient energy based on the size and material of the part. Care must be taken to ensure that this frequency is above the critical frequency of the part for efficient heating.
This is the cycle-to-cycle repeatability of the induction power supply in manufacturing given standard incoming voltage variations and other tolerances.
This should be the same every cycle to reach the same temperature on the insert.
This is dependent on the fixturing and handling device. Varying placement of the insert inside the induction coil will result in inconsistent temperatures of the insert.
The location of the insert in the hole of the plastic part is determined by insert pressure. Lower pressure leaves the insert above the required location, whereas higher insertion pressure may cause undesirable “flash” of the plastic material.
The diameter of the insert hole must be the correct size to allow the plastic to flow around the insert. If the hole is too small, extra plastic will be displaced.
Cool down following the insertion cycle is needed to anchor the insert inside the plastic part. If the cool-down time is too short and the insertion pressure is removed quickly, inserts will often be pushed out of the plastic part.
The installation temperature of the insert is a key factor in the success of the staking process. Each insert must be heated to the same temperature in the same time to achieve a consistent process.
For more information, visit our metal-to-plastic page, which has numerous application notes. Complimentary lab testing is available from Ambrell's applications laboratories, where the applications team will put their decades of induction experience involving thousands of applications to work for you. Want to read more about metal-to-plastic applications? Read our informative white paper!

Induction heating, a process that uses electromagnetic induction to heat electrically conductive materials, is often thought of for large industrial...

Objective A company had been using a flame for brazing copper assemblies to make electrical components, but they contacted THE LAB at Ambrell because...
Induction heating is a highly efficient and versatile technology with numerous industrial applications. Unlike traditional heating methods that rely...